Healthy eating involves increasing the amount of fresh organic vegetables and fruits in your diet, eating raw whenever possible. Vegetables and fruits are the most alkaline of foods. Include more high-alkaline foods in your diet to balance your intake of important healthy acid-forming foods such as organic meat, wild-caught fish, raw nuts, and gluten-free grains. A high-alkaline foods diet is important for anyone dealing with inflammatory conditions, and especially those using High pH Therapy.
The words “alkaline or alkalizing” and “acidic or acidifying” represent the food’s effect on the body and not the actual value of the food itself. Different value systems have been designed to quantify this effect. The charts below are provided as a general guide for those trying to improve their heath through diet change.
The PRAL formula is a scientific way to measure the potential renal acid load of any food based on the protein, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and calcium content of a 100 gram (3.5 oz.) serving. Negative (-) numbers are good numbers and indicate the potential alkalinity being contributed by a base-forming food. Positive (+) numbers indicate the potential acidity being contributed by an acid-forming food.
There are many minerals that are also alkaline and have an alkalizing affect in the body. These alkaline minerals can be taken as supplements to support an alkaline diet. Alkaline minerals include magnesium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, germanium, and cesium.
Check out these free alkaline foods charts and other helpful nutrition charts.
• Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™ Food Chart
• PRAL Values Chart
• Foods To Avoid with pH Therapy
• Tyramine-Containing Foods Chart
• Selected Potassium-Rich Foods Chart
Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™ Food Chart
PRAL values given are for a 100 gram (3.5 ounce) serving size.
Values for larger or smaller servings must be adjusted accordingly.
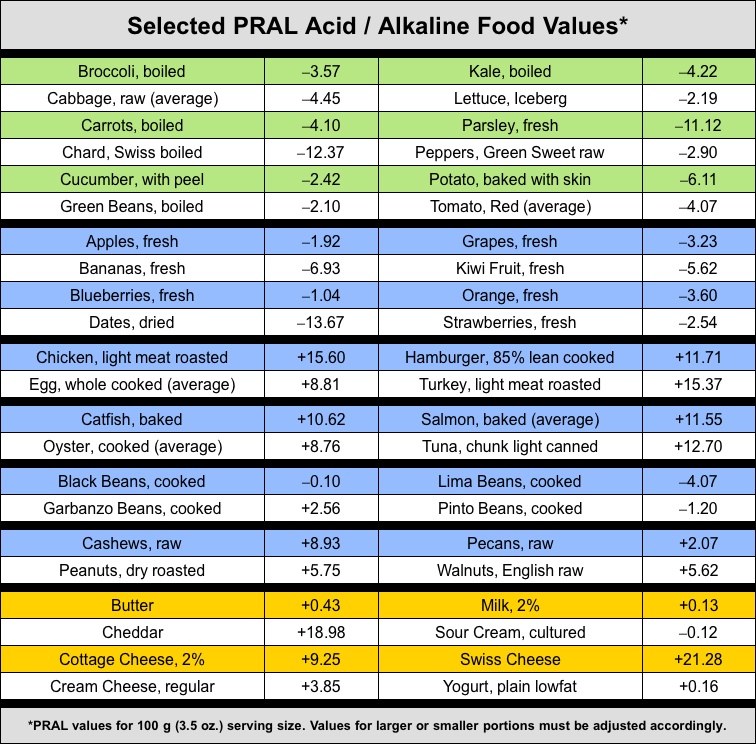
Chart Information Source: Alkaline Diet Chart / Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™
THIS CHART DESIGNED BY ESSENSE-OF-LIFE, LLC
All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission of Essense of Life, LLC.
PRAL Average Values Chart
PRAL values given are for a 100 gram (3.5 ounce) serving size.
Values for larger or smaller servings must be adjusted accordingly.
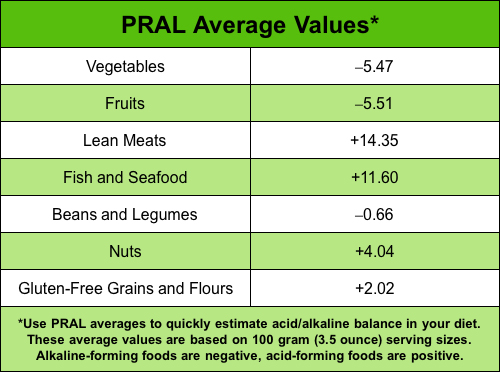
Chart Information Source: Alkaline Diet Chart / Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™
THIS CHART DESIGNED BY ESSENSE-OF-LIFE, LLC
All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission of Essense of Life, LLC.
https://blog.essense-of-life.com/featured-product-the-alkaline-balance-food-chart/
Foods To Avoid for High pH Therapy
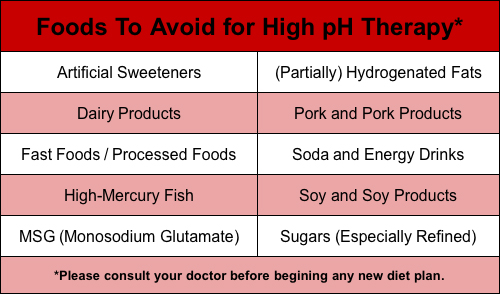
Chart Information Source: Alkaline Diet Chart / Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™
THIS CHART DESIGNED BY ESSENSE-OF-LIFE, LLC
All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission of Essense of Life, LLC.
Tyramine-Containing Foods

Chart Information Source: Alkaline Diet Chart / Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™
THIS CHART DESIGNED BY ESSENSE-OF-LIFE, LLC
All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission of Essense of Life, LLC.
Selected Potassium-Rich Foods Chart
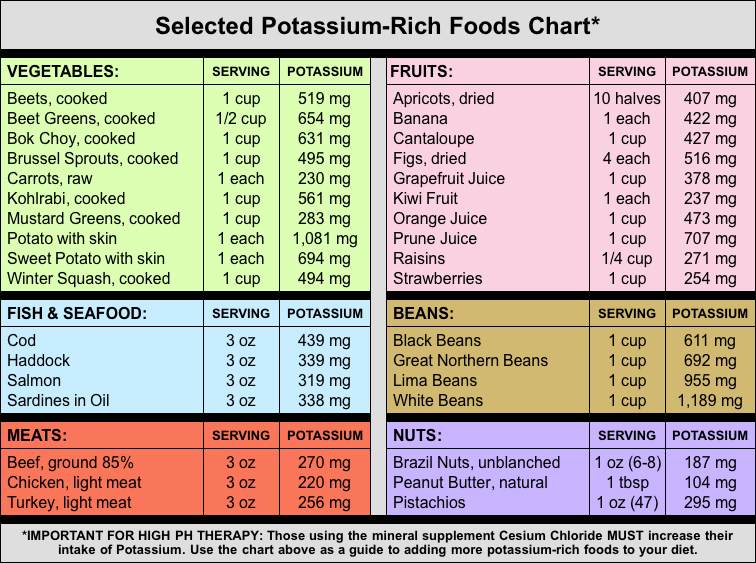
Chart Information Source: Alkaline Diet Chart / Alkaline-Balance Target Diet™
THIS CHART DESIGNED BY ESSENSE-OF-LIFE, LLC
All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission of Essense of Life, LLC.
Alkaline Foods Resources
Alkaline/Acidic Food Chart
These charts are a basic guideline for those trying to adjust their diet by eating fewer acidic foods and more alkaline foods.
Understanding pH
pH is actually an exponential scale. Every unit change in pH equals a 10-fold increase or decrease in acidity (or basicity). Thus, dropping from pH 7 to 6 is a 10-fold increase in acidity. However, dropping further to pH 5 is another 10-fold increase, or a 100-fold increase (10 x 10 = 100) in acidity from pH 7. For this reason, even minor deviations in pH around the more extreme values constitute much greater changes in acidity (or basicity) than seemingly major changes around the neutral mark. For example, merely dropping from pH 3.1 to 3.0 equals an increase in acidity more than 238 times greater than dropping from pH 7 to 6.
The pH Problem
Explains some differences in blood, urine and saliva pH measurements.
Acid and Alkaline in the Diet
When nutritionists talk about acid- or alkaline-forming foods, they are referring to the condition of the food after ingestion. There are many food substances which are acidic in their natural form that become alkaline when broken down within the body. Excellent article.
Acid/Alkaline: Clearing Up The Confusion
The purpose of this article is to clearly and simply explain the meaning of acid and alkaline and to explain why a study of the acid-alkaline balance, or pH balance, is important in the study of health and healthful living. Excellent article.
Acid-Base Balance
Many of the enzymes that facilitate metabolic reactions operate optimally only in solutions of specific alkalinity. When there is a deviation from this level of alkalinity, whether higher (referred to as alkalosis), or lower (referred to as acidosis), severe malfunctions can occur. These malfunctions are manifested by slower enzymatic reactions, and thus a decrease in synthesis of specialized molecules, such as vitamins, proteins, etc. There is also an impairment of the production of ATP molecules that are needed for energy and are made from glucose.
Basic Acid-Alkaline Food Chart Introduction
The effect of food on the body is nothing to do with the pH of the food itself. The important measurement is how the food changes the pH of your body after it has been digested. Often sour foods like lemon juice will actually raise pH after digestion, making the body more alkaline. Alkalizing the body with food does not mean that you must stop eating lots of different foods. The opposite is true. You must eat a wide variety of food, choosing acidifying foods as well as alkalizing ones, which, in total, have an overall alkalizing effect. The tables that I present here focus solely on the acid / alkali affect of food after it has been digested.
The pH / Digestion / Elimination Axis
Enzymes function optimally at a specific pH and become inactive if this deviates beyond narrow limits. Enzymes are vital substances. Without them, the chemical reactions necessary for life could not take place. All of the best and most nutritious food in the world and the most expensive vitamin pills and supplements won’t get digested and assimilated right if your body pH is off balance.
Essential Details on Acid and Alkaline-Forming Effects of Food and How Your Body Maintains a Healthy pH
Most carbonated soft drinks (sodas) have a pH of about 3, making them about ten thousand times more acidic than pure water (pH of about 7). When you ingest foods and liquids, the end products of digestion and assimilation of nutrients often results in an acid or alkaline-forming effect. Highly processed foods (like white flour products and white sugar) have an acid-forming effect on your system. In addition, a number of different acids are formed and released into your body which are generated by your everyday metabolic activities. Your body has three major mechanisms (buffering systems) to prevent these dietary and metabolic acids from shifting the pH of your blood (plasma) outside of the 7.35 to 7.45 pH range needed for your cells to function properly. If you spend years eating a diet that is mainly acid-forming, you will overwork some of the buffering systems to a point where you could create undesirable changes in your health. It is in your best interest to follow a diet that does not create unnecessary work for your buffering systems.
Introduction to pH
pH is the acronym for potential hydrogen. It is a measure of the degree of saturation of the hydrogen ion in a substance or solution. H3O (hydronium ion+) is the acid element and OH- (hydroxyl ion-) is the base or alkaline element. When the H3O and OH- are out of balance, a pH meter will detect this and the reading will move above or below 7 (neutral). If one goes up the other goes down and vice versa. In the human body, a pH balancing act is continuously going on to maintain homeostasis.
pH Range
In general, you want pH of urine to be below 6.5 and saliva to be above 6.5. High urine pH is not good. It should always be able to get down into the 5 range – this shows metabolic acids can and are being removed from the system.
Covering Nutritional Bases: The Importance of Acid-Base Balance
Every cell of the body functions optimally within a certain pH range (pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the body). Since the body must, at all costs, operate at a stable pH, any dietary acid load has to be neutralized by one of a number of homeostatic base-producing mechanisms. Since calcium is a strong base and bone contains the body’s largest calcium store, metabolic acidosis causes a release in calcium from bone. Glutamine acts much like calcium to neutralize the body’s acidosis. Since skeletal muscle contains the body’s largest glutamine store, metabolic acidosis causes muscle breakdown to liberate glutamine from the muscle.
CONTAINS REFERENCES
Diet: You Are What You Eat
Everything we eat affects the health and well-being of our body. Most calls to “change your diet” to improve your health include these recommendations: eat whole, unprocessed foods (raw fruits, raw vegetables, whole grains); drink plenty of clean water (not tap or filtered); and reduce or eliminate intake of refined sugar and flour products, coffee, soft drinks, margarine, commercial cooking oils, dairy and other animal products. In processed foods, heat destroys some of the nutrient value, including destroying enzymes and reducing vitamin and antioxidant content.
pH of Living Systems on Wikipedia
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. The pH of different cellular compartments, body fluids, and organs is usually tightly regulated in a process called acid-base homeostasis. The pH of blood is usually slightly basic with a value of pH 7.4. This value is often referred to as physiological pH in biology and medicine. Enzymes and other proteins have an optimum pH range and can become inactivated or denatured outside this range. The most common disorder in acid-base homeostasis is acidosis, which means an acid overload in the body, generally defined by pH falling below 7.35.
Dietary Potential Renal Acid Load and Renal Net Acid Excretion in Healthy, Free-Living Children and Adolescents
Experimental studies in adults showed that renal net acid excretion (NAE) can be reliably estimated from the composition of diets. PRAL (mEq/d) = 0.49 x protein (g/d) + 0.037 x phosphorus (mg/d) – 0.021 x potassium (mg/d) – 0.026 x magnesium (mg/d) – 0.013 x calcium (mg/d). There is increasing evidence that acid-base status has a significant effect on high-intensity physical performance, urolithiasis, and calcium metabolism.
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH
About High pH Therapy
High pH therapy focuses on using a combined nutrition and supplement approach to balance body pH by reducing the load on the overworked buffering system. The alkaline diet focus of pH therapy is of particular importance for those needing intense nutritional support when dealing with cancer and other ailments.
All About Dietary Acids and Bases
When a food is ingested, digested, and absorbed, each part of that food will present itself to the kidneys as either an acid-forming compound or an alkaline-forming one. It’s the kidneys’ job to adjust the pH to a constant level by changing either what they secrete, and/or how they filter things.
Alkalizing Minerals
Essense of Life carries a range of alkalizing minerals. Alkalizing minerals are the basis of High pH Therapy and may also be used as part of an alkaline-style diet.
Do You Have Cancer? Looking for Options? Why Alkaline
All cancers have certain key characteristics in common. Unlike healthy cells which have a very efficient aerobic (with oxygen) metabolism, cancer cells use anaerobic (without oxygen) metabolism. Anaerobic metabolism relies on the fermentation of glucose (sugar) for fuel, which is a very inefficient process that not only creates an energy drain on the body, but also creates an excess of acidic lactic acid as a waste product. Low oxygen = anaerobic metabolism = glucose fermentation = acidic waste = low pH. An alkaline diet addresses all of these common cancer characteristics.
This article is copyright ©2018 Essense of Life, LLC. All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission.
The information contained herein is not medical advice and is not intended to replace the advice or attention of your personal physician or other health care professionals. Consult your doctor or health care professional before making any changes to your diet or starting a supplement program.
Facebook Comments