Keto Diet versus Alkaline Diet, Which is Right for You?

Keto Diet? Alkaline Diet? What’s all the buzz about? And which diet is right for me?
Explore the buzz surrounding the Keto Diet and Alkaline Diet to find the one that aligns with your health goals. Uncover the benefits, and potential drawbacks of each diet, empowering you to make an informed decision tailoring a diet plan that fits your lifestyle.
Whether you’re seeking weight loss, improved energy, or overall well-being, our comprehensive comparison guide breaks down the key differences and similarities between these popular diets. Navigate the world of nutrition confidently and discover which path – Keto or Alkaline – is the right fit for you.
Comparing the Keto Diet and Alkaline Diet: A Comprehensive Guide
There is no question, there are literally hundreds of diet plans out there. Among those available, the Keto Diet and Alkaline Diet stand out as popular choices, each offering unique approaches to health and wellness. Discover the secrets of these diets and determine which one is the best fit for you. Whether you’re aiming for weight management, increased energy, or overall well-being, our guide provides valuable insights to help you make an informed decision for your health journey.
The Ketogenic Diet: Principles and Benefits
Principles: The Ketogenic Diet, often referred to as the Keto Diet, is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. The primary aim is to shift the body’s metabolism from carbohydrates to fats, entering a state known as ketosis. This metabolic state enables the body to burn fat for fuel more efficiently.
Key Components:
- High Fat: About 70-80% of daily calories come from fats.
- Moderate Protein: Approximately 20-25% of daily calories come from protein.
- Low Carbohydrates: Only about 5-10% of daily calories come from carbs, typically less than 50 grams per day.
Benefits:
- Weight Loss: Rapid weight loss due to the body’s increased ability to burn fat.
- Improved Energy Levels: Stable energy levels as the body uses fat for a consistent energy supply.
- Enhanced Mental Clarity: Reduced carb intake can lead to improved cognitive function and focus.
- Blood Sugar Control: Lower carbohydrate intake helps manage blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
Considerations:
- Keto Flu: Initial side effects like fatigue, headache, and irritability as the body adjusts to ketosis.
- Nutrient Deficiency: Potential for deficiencies in vitamins and minerals if not properly managed.
- Sustainability: Strict dietary regimen may be challenging to maintain long-term.
The Alkaline Diet: Principles and Benefits
Principles: The Alkaline Diet focuses on consuming foods that have an alkalizing effect on the body, aiming to maintain the body’s pH balance. The theory is that modern diets high in acid-producing foods can lead to health issues, and an alkaline diet can help counteract this.
Key Components:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Emphasis on high consumption of fresh produce.
- Nuts and Seeds: Encouraged as part of the diet.
- Whole Grains and Legumes: Preferred over processed grains.
- Limited Acidic Foods: Reduction of meat, dairy, processed foods, and refined sugars.
Benefits:
- Improved Digestion: High fiber intake from fruits and vegetables aids digestive health.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Balanced pH levels can lead to increased vitality and energy.
- Inflammation Reduction: Alkaline foods are believed to help reduce inflammation in the body.
- Bone Health: The diet’s emphasis on plant-based foods may support bone health by providing essential nutrients like magnesium and calcium.
Considerations:
- Scientific Support: Limited scientific evidence directly supporting the diet’s effect on body pH and overall health.
- Dietary Restrictions: May be challenging to follow due to significant restrictions on commonly consumed foods.
- Nutritional Balance: Important to ensure adequate intake of protein and other essential nutrients.
Making the Right Choice for You
Choosing between the Keto Diet and the Alkaline Diet depends on your individual health goals, lifestyle, and preferences. Here are some factors to consider:
- Weight Management: If rapid weight loss and improved insulin sensitivity are your primary goals, the Keto Diet may be more effective.
- Overall Well-being: If you aim for a diet rich in fruits and vegetables with potential anti-inflammatory benefits, the Alkaline Diet might be more suitable.
- Sustainability: Consider which diet aligns better with your lifestyle and which dietary restrictions you can maintain in the long term.
Conclusion
Both the Keto Diet and Alkaline Diet offer unique benefits and approaches to health and wellness. By understanding their principles, benefits, and considerations, you can make an educated decision that aligns with your health goals. Whether you choose the fat-burning prowess of the Keto Diet or the plant-based focus of the Alkaline Diet, the key is to find a sustainable and balanced approach that works for you. Explore these trending diets and embark on the right dietary path for your health journey.
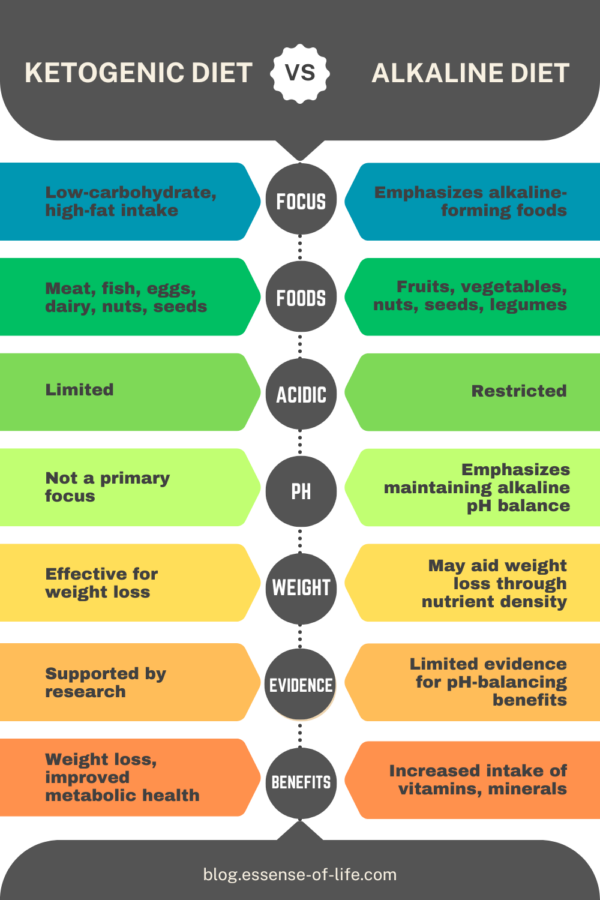
Here’s a simplified comparison chart highlighting key aspects of the keto diet versus the alkaline diet:
| Aspect | Keto Diet | Alkaline Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Low-carbohydrate, high-fat intake | Emphasizes alkaline-forming foods |
| Primary Foods | Meat, fish, eggs, dairy, nuts, seeds | Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes |
| Acidic Foods | Limited | Restricted |
| pH Balance | Not a primary focus | Emphasizes maintaining alkaline pH balance |
| Weight Loss | Effective for weight loss | May aid weight loss through nutrient density |
| Scientific Evidence | Supported by research | Limited evidence for pH-balancing benefits |
| Potential Health | Weight loss, improved metabolic health | Increased intake of vitamins, minerals |
This chart provides a snapshot of the key differences between the keto and alkaline diets, helping individuals make informed choices based on their health goals and dietary preferences.
The Ketogenic Diet Basics
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet designed to induce a state of ketosis in the body, where it burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Foods to Eat
Here are foods commonly allowed on a keto diet:
- Meat: Beef, pork, lamb, poultry, and other meats.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, trout, tuna, and mackerel.
- Eggs: Preferably pasture-raised or omega-3 enriched.
- Dairy: High-fat dairy products like butter, cream, and cheese.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds.
- Healthy Oils: Olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, and other healthy oils.
- Avocados: A rich source of healthy fats.
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, zucchini, and peppers.
- Berries: In moderation, as they are lower in carbohydrates (e.g., strawberries, blueberries).
- Cheese: Hard cheeses, cream cheese, and other high-fat cheeses.
- Plain Greek Yogurt: Full-fat and unsweetened varieties.
- Butter and Cream: Used for cooking and adding fat to meals.
- Condiments: Herbs, spices, and low-carb condiments like mustard and mayonnaise.
- Low-Carb Sweeteners: Stevia, erythritol, and monk fruit can be used in moderation.
It’s important to note that the key to a successful keto diet is maintaining a low carbohydrate intake (usually around 20-50 grams per day) to stay in ketosis. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Foods to Avoid
On a ketogenic diet, it’s essential to limit or completely avoid certain foods that are high in carbohydrates to maintain a state of ketosis. Here are foods to avoid on a ketogenic diet:
- High-Sugar Foods: This includes sugary beverages, candies, cakes, and other sweets.
- Grains and Grain Products: Wheat, rice, oats, corn, and products made from them (bread, pasta, cereal).
- Starchy Vegetables: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, and other high-carb vegetables.
- Fruits: Most fruits are high in sugars and carbs, so limit their intake. Berries in moderation are an exception.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, and peas are relatively high in carbohydrates.
- Sugary Sauces and Condiments: Avoid high-sugar ketchup, BBQ sauce, and other sugary condiments.
- Low-Fat or Diet Products: These often contain added sugars to compensate for the reduced fat content.
- Processed Foods: Many processed foods, even those labeled as low-carb, may contain hidden sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Alcohol: Alcoholic beverages can be high in carbs and may interfere with ketosis.
- Some Dairy: Be cautious with milk and yogurt, as they can contain more carbs. Opt for full-fat and unsweetened options.
- Trans Fats: Avoid processed foods containing trans fats, as they can be detrimental to health.
- High-Carb Sauces: Be mindful of sauces like teriyaki, honey mustard, and others high in sugar.
- Highly Processed Vegetable Oils: Vegetable oils like soybean oil and canola oil are high in omega-6 fatty acids and best limited.
It’s crucial to read food labels carefully, be aware of hidden sugars, and track your daily carbohydrate intake to maintain ketosis effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Alkaline Diet
The alkaline diet is based on the concept that certain foods can affect the acidity or alkalinity (pH) of the body. Advocates of the alkaline diet believe that consuming alkaline-forming foods can help maintain the body’s optimal pH balance, which is slightly alkaline, and promote overall health.
The diet primarily emphasizes eating foods that are alkaline or alkaline-forming, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes. These foods are believed to help reduce the acidity levels in the body and create a more alkaline environment.
Foods to Eat
Some key principles of the alkaline diet include:
- High Consumption of Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are typically alkaline-forming and are central to the alkaline diet. Emphasis is placed on consuming a variety of colorful produce to maximize nutrient intake.
- Limiting Acidic Foods: Acidic foods, including meat, dairy, processed foods, refined grains, and caffeine, are restricted or minimized in the alkaline diet. These foods are believed to contribute to acidity in the body.
- Drinking Alkaline Water: Some proponents of the alkaline diet advocate for drinking alkaline water, which has a higher pH level than regular water. They believe that alkaline water can help neutralize acidity in the body.
- Emphasizing Whole Foods: Whole, unprocessed foods are favored on the alkaline diet, while processed and refined foods are discouraged.
- Maintaining Hydration: Staying adequately hydrated is essential on the alkaline diet, and proponents often recommend drinking plenty of water to support overall health and pH balance.
The alkaline diet emphasizes consuming foods that are believed to promote alkalinity in the body, aiming to maintain an optimal pH balance. It prioritizes fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes while limiting acidic foods such as meat, dairy, processed items, and caffeine. Alkaline water is sometimes recommended to support pH balance. However, scientific evidence supporting the diet’s claims is limited, and the body’s pH regulation mechanisms are complex and not solely influenced by diet. As with any diet, moderation and overall nutrient intake are crucial factors for health. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is advisable for personalized dietary guidance.
Foods to Avoid
On the alkaline diet, it’s recommended to avoid or limit acidic foods, including:
- Meat and poultry
- Dairy products
- Processed foods
- Refined grains and flour
- Sugary snacks and desserts
- Artificial sweeteners
- Caffeinated beverages
- Alcohol
- Processed oils and fats
These acidic foods are believed to potentially disrupt the body’s pH balance and overall health.
Final Thoughts: Weighing the Alkaline Diet’s Focus on pH Balance and Food Choices
When comparing the keto and alkaline diets, the alkaline diet prioritizes consuming alkaline-forming foods such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes while limiting acidic foods. Advocates suggest that alkaline-forming foods help maintain the body’s optimal pH balance and promote overall health. However, scientific evidence supporting the alkaline diet’s efficacy is limited. While the alkaline diet emphasizes nutrient-rich whole foods, its impact on health outcomes remains unclear compared to the well-researched ketogenic diet, which focuses on low-carbohydrate, high-fat intake to induce ketosis and has demonstrated efficacy in weight loss and certain health conditions. Ultimately, individual dietary needs and preferences should guide the choice between the two diets.
This article is copyright ©2019 Essense of Life, LLC. All rights reserved. Do not copy without permission.
This information is not medical advice and is certainly not intended to replace the advice or attention of your personal physician or other healthcare professional. Therefore, consult your doctor or healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or starting a supplement program.




Facebook Comments